Researchers develop a trilayer TMD heterostructure with interlayer excitons
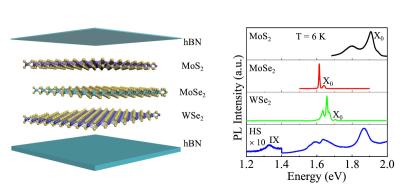
Researchers from China's Tsinghua University developed a novel material, made from a stack of 2D materials, that offers interlayer excitons, useful for valleytronics applications.
The new material is a trilayer TMD heterostructure, composed of molybdenum and sulfur, molybdenum and selenium, and tungsten and selenium. Using photoluminescence spectroscopy, the researchers confirmed the presence of interlayer excitons and described various properties and requirements of the phenomenon.